FIRST WebAdmin Help Version 2.16 © 2012 FIRST Software Solutions Pty Ltd
Boolean AND and OR buttons are available to refine search criteria.
Operator |
Meaning |
AND |
combines two or more criteria entered |
OR |
searches for either criteria entered |
Enter the first component of the search criteria. The search criteria is displayed in the SQL window
Click AND or OR button
Enter the second search criteria
Repeat for further criteria
Click SEARCH
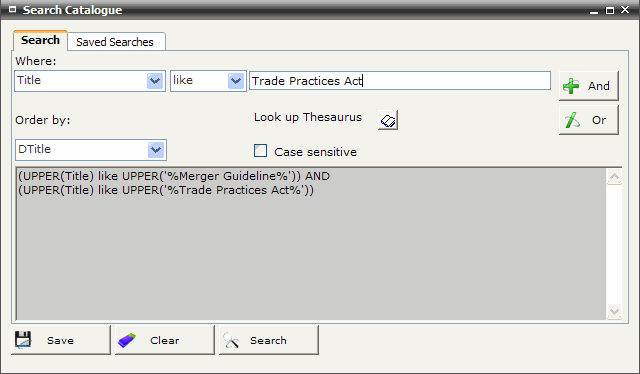
For example: Search for Title relating to ‘Merger Guidelines in the Trade Practices Act’
Select Title from the Where: pop-up list
Select Like from comparison operator pop-up list to search for the title as a string
Enter Trade Practices Act
Click AND Boolean operator
Enter Merger Guideline (the system automatically truncates the beginning and end of a string. In this case guideline and guidelines will be retrieved)
The search string is displayed at the SQL window, connected by the AND operator
Click SEARCH

Tip:
|
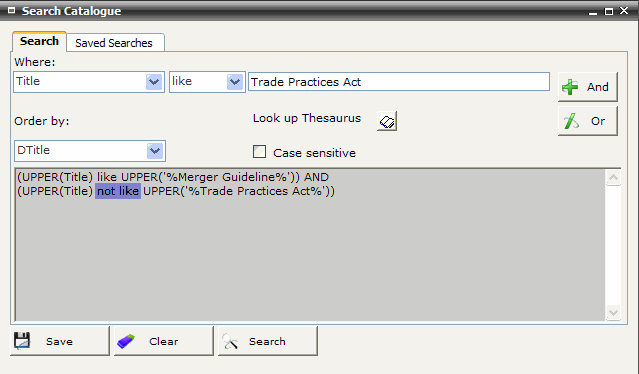
For example: Search Title using the Boolean NOT operator
Select Title from the Where: pop-up list
Enter the first component
Select Like from the comparison operator pop-up list
Click AND
Select Not Like from the comparison operator pop-up list
Enter the second component
Click SEARCH
FIRST has no order of precedence in relation to the Boolean operators AND and OR i.e. precedence is determined by the position in the search string.
A search string can be either typed into the SQL window on a Search screen in FIRST or constructed by selecting fields from the Where: pop-up list, comparison operators from the comparison operator pop-up list, entering search criteria in the data entry box and selecting Boolean Operators.
The constructed search string is read by the computer from left to right. However, the parsing engine, which calculates or valuates the search string, reads the SQL search string right to left. The effect of this is illustrated below:
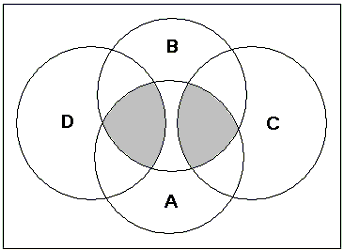
For example, a search string:
‘A AND B AND C OR D’ will be calculated as (A AND (B AND (C OR (D))
In other words all records matching ‘C OR D’ will be retrieved first. Then all records from this initial set that also match ‘B’ will be retrieved. This second set will then be combined with all records matching ‘A’ to generate the final search result.
The Venn diagram below illustrates the final set of records retrieved.
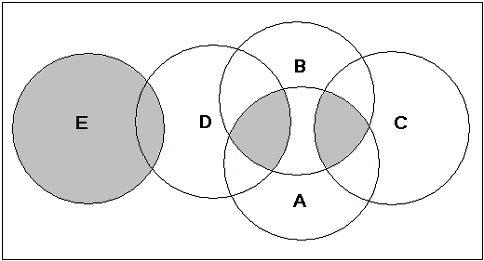
If you enter parenthesis to enforce nested Boolean logic then the nested components are again calculated or valuates right to left.
For example, a search string:
((A AND B) AND (C OR D)) OR E
All records matching ‘E’ are retrieved first. Then records matching both ‘C OR D’ are added to the records matching ‘E’. ‘This set (C OR D) OR E’ is added to all records matching ‘A AND B’ to create a final search result.
The Venn diagram below illustrates the final set of records retrieved.